Pre-clinical
The preclinical evaluation of the PD-Curcumin device for treating burns and ulcers demonstrated highly promising results compared to the gold standard, sulfadiazine-silver cream. After 14 days of treatment, PD-Curcumin (noted as PL-Pro nanocurcumin) showed statistically superior skin regeneration compared to both the control vehicle and sulfadiazine-silver cream (Fig. 1) Furthermore, hydroxyproline concentration analysis revealed a significant improvement in skin regeneration. As a critical component of collagen synthesis and deposition, hydroxyproline plays an essential role in wound healing and tissue repair.
After 21 days of treatment with our formula, the treated mice exhibited statistically higher hydroxyproline levels compared to the groups treated with sulfadiazine-silver cream and the control vehicle, indicating enhanced collagen production and accelerated skin repair (Fig. 1B) From a safety perspective, systemic toxicity assessments were conducted on the liver (ASAT/ALAT/Bilirubin), blood (white cells, red cells, albumin), and renal system (creatinine). The results confirmed no signs of toxicity following the administration of our device.
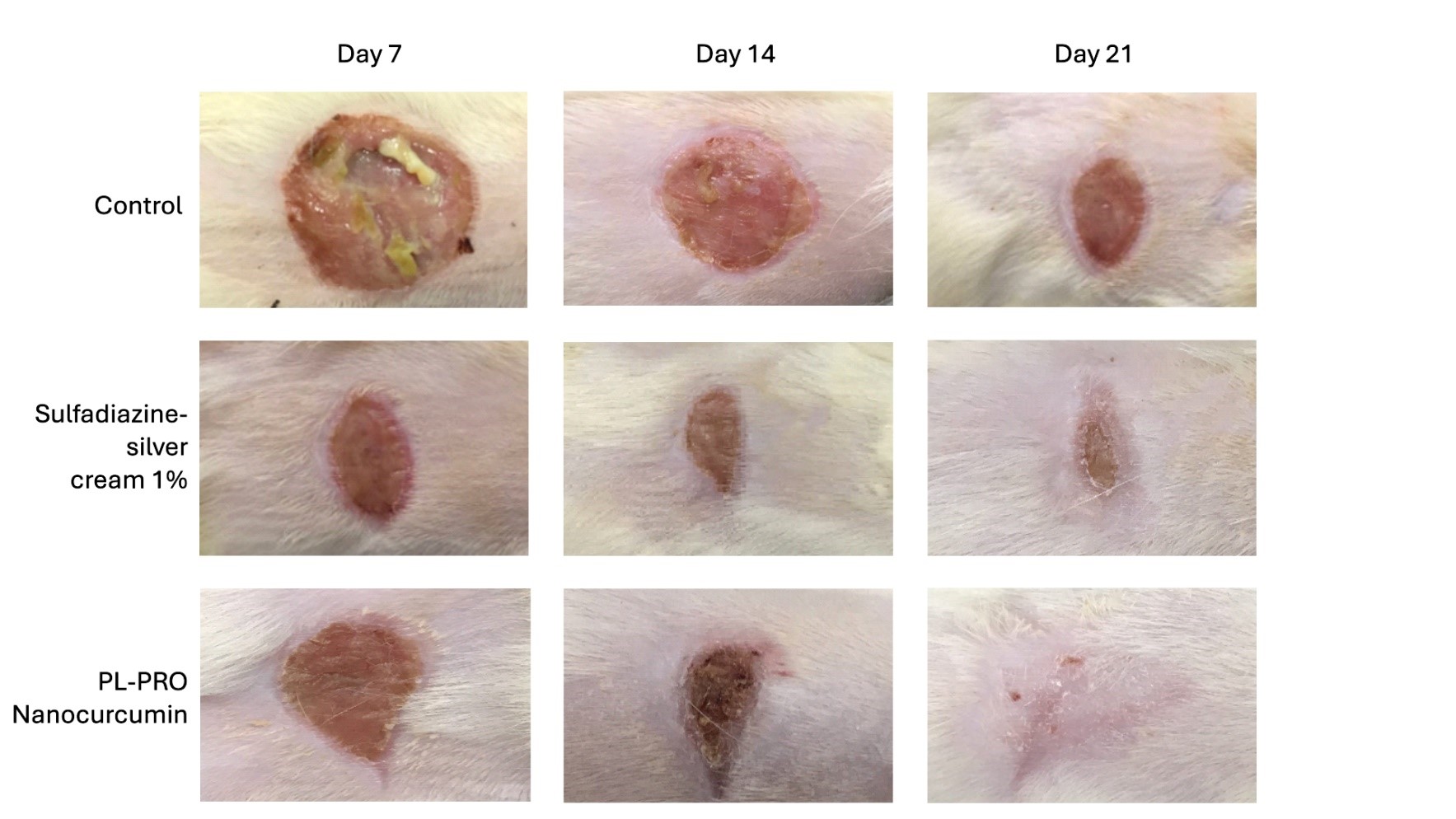
Fig 1. Macroscopic images of burned mice treated with the control vehicle, 1% sulfadiazine-silver cream, or PD-Curcumin (PL-PRO Nano Curcumin)
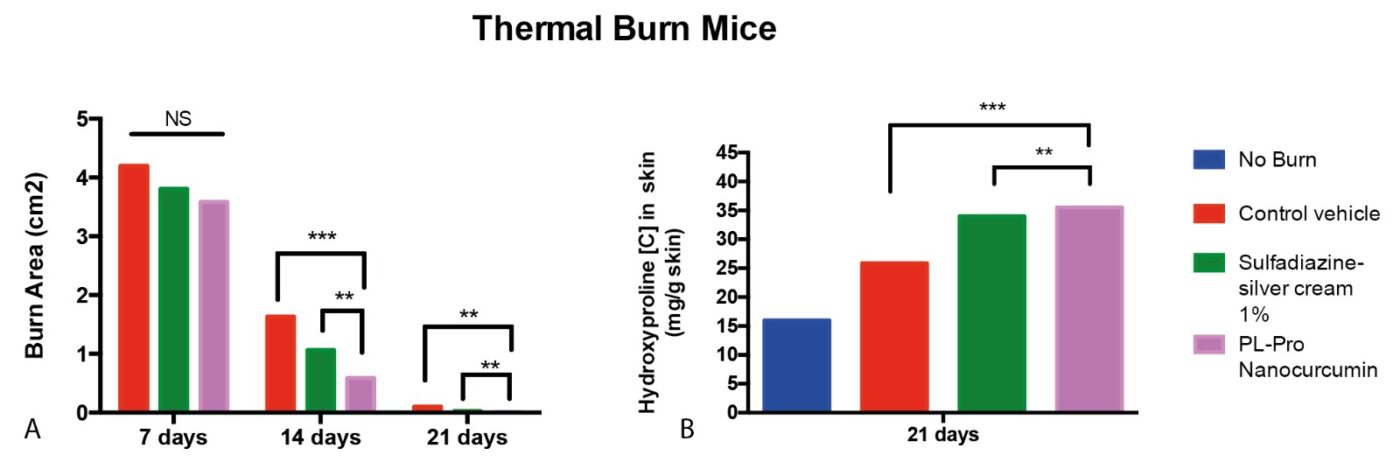
Fig 2.A: Effects of Sulfadiazine-silver cream and PL-Pro Nanocurcumin on the size of the wounded area in thermal burned mice model.
2.B: Effects of Sulfadiazine-silver cream and PL-Pro Nanocurcumin on hydroxyproline content in skin tissues in thermal burned mice model. Data were expressed as the mean. Two-way ANOVA test, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ns (non-significant) P > 0.05.

